introduction Information security overview Version: 1.0.2 On this page
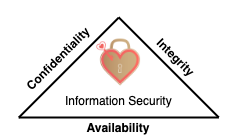
Information security overview Protecting information and information systems. Defines sets processes and activities performed in order to protect information. Goal is to prevent unauthorized users from stealing and misusing information or services.If sensitive information falls in wrong hands, it may cause huge losses includingfinances, brand reputations, customers. Essential terms Hack value Hackers' evaluation of whether something is worth or interesting. High hack value examplesAccessing peoples credit card information as it can generate money. Just accessing peoples names just to show a difficult task is doable. Vulnerability Weakness which can compromise the system and be used for a possible attack. E.g.a policye.g. policy regulating whether a personal should stick in USB drives to computer laptops. design/implementation errorse.g. Linux + macOS + Windows are susceptible to a vulnerability where an USB drive that disguises as keyboard and have greater access on computer Exploit Breach through vulnerabilities. Also refers to a software that allows taking advantage of identified vulnerabilities. E.g. connecting a malicious USB. Payload Part of malware or exploit code. Used for e.g.Creating backdoor s in victims machine Damaging or deleting files Committing data Hijacking a computer E.g. a keylogger or a RAT (Remote Administration Tool) that a malicious USB installs. Zero day attack Also known as • zero-day attack 0-day attack 0 day attack Exploiting previously unknown vulnerabilities before patch is released. Zero day vulnerability Hole in software that is either 1 Unknown to the one that's interested in mitigating in (e.g. vendor) Known but patch has not been developed Targeted attacks often include zero-day vulnerabilities 3 ❗ A vulnerability is not zero day once it's disclosed and patched Zero-day exploit Taking advantage of zero-day vulnerabilities Often done by using malware 3 FlowAttacker discovers the vulnerability Attacker exploits vulnerability Attack happens (called day zero) Vendor learns about vulnerability Patch is createdSometimes vendor may not patch it e.g. if software is outdated or has no support. Patch is applied❗ Sometimes they're not!E.g. home routers has vulnerabilities that has been known for years as ISPs do not usually configure routers after setup 💡 Time frame between patch is created and applied is used by malicious hackers to maximum extend.Many times corporations are slower to react which causes harm. Window of vulnerability (WOV) Time from vulnerability is discovered until most vulnerable systems are patched 1 Often measured in days e.g. 28 days. E.g. Spectre & Meltdown Vulnerabilities in AMD and Intel CPUs Can be exploited to elevate the privileges in the given system. Still exists but no longer a zero day. Affected all cloud providers, they needed to run firmware updates, updates provided by Intel that caused delays. Daisy chaining An attack in which hackers gain access to one network/device and then using it to access next networks/devices. Steps Hackers gain access to a device within your system/networke.g. smartwatch, refrigerator, PC. They move further by gaining access to next device in your network and then next and so on.Potentially hacker owns the network in the end. 🤗 Example for hacking banks or similar Go after person that has the most access. Hack that persons home router as attack vector.Because it has the least resistance compared to corporate network.Corporate network: has corporate firewalls, IT stuff, policies etc. Home router: Rarely updated, full of vulnerabilities. They usually run down-sized linux operating system. An attack vector is a method or pathway used by a hacker to access or penetrate the target system. Scan devices that are connected to the router.Can see communication (can be encrypted) but always sees ports, URLs, addresses being used. E.g. mans PC, wifes PC, smart TV/refrigerator, his cell phone, wifes cell phone etc. Attack with different attack vector options:Change the DNS settings, you can set yourself as DNS. Put his computer to DMZ to expose his PC for access from outside world. Apply phishing, exploits to the operating system of the devices. Get access to one of the systemsE.g. an Android phone. They have many vulnerabilities.They don't get updates after a while. If they exceed design limits e.g. when operating when it's hot outside, then the hardware flaws occurring causes exploitable software attacks such as Bitsquatting Get access toInformation such as bank accounts, credit card details After infecting one device, jump other devices in bank network if e.g. the mobile phone is also used in bank network. Doxing Finding and publishing someone's personally identifiable information (PII) for malicious reasons. E.g. an individuals name, e-mail address or sensitive data of an organization. E.g. confidential government files get leaked to the public. StepsGather private and valuable information about a person/organizationE.g. photographs, SSN, social accounts, address... Build a profile of target by learning more information e.g. through social media. Misuse collected information for different reasons.E.g. identity theft, stealing financial information to use, coercing their target's into doing something they don't want to Bot Contraction of "robot" A software that can be controlled to execute predefined tasks. Used by hackers to control the infected machines for malicious reasons. Use-caseE.g. using a bot to control the computer and perform attacks on other computers E.g. creating a botnet by infecting more machines CIA triad Also known as three principles of information security Recognized widely as hearth (main focus) of information security Should function as as goals and objectives for every security program 📝 Ensures Confidentiality Ensures that information is available only to people who are authorized to access it. Improper data handling or a hacking attempt leads to confidentiality breaches. 💡 Controls: • encryption • classification • access control • proper disposal (e.g. of DVDs, CDs, etc.) Integrity Ensures the accuracy of the information Prevents improper and unauthorized changes—the 💡 Controls: • hashing • access control Availability Ensuring resources are available whenever the authorized user needs them 💡 Controls: • redundancy • data back-ups • antivirus • DDoS prevention Authenticity Ensures the quality of being genuine or uncorrupted, either:users are actually who they present themselves to be through authenticationor a document or information presented is not corrupted. 💡 Controls: • users (biometrics) • smart cards • data (digital certificates ) Non-repudiation 📝 Guarantee thatsender of a message cannot deny having sent the message recipient cannot deny having received the message 💡 Controls: digital signatures, logging Functionality, usability, security triangle ComponentsFunctionality : the features of the systemUsability : GUI of the system and how user friendly it is.Security : How the processes of the system are used and who is using them InterconnectedAny change made to one component directly affects decreases the other two. E.g. if the system security is increased, then the functionality and usability of the system are decreasedBecause of greater overhead of security with more checks or through greater examination. 💡 Balance each and every one of them to get the desired levels of security, functionality, and usability. Document types Standard Mandatory rules used to achieve consistency Baseline Provide the minimum security level necessary. Guideline Flexible, recommended actions users are to take in the event there is no standard to follow. Procedure Detailed step-by-step instructions for accomplishing a task or goal