cloud-computing Cloud computing Version: 1.0.2 On this page
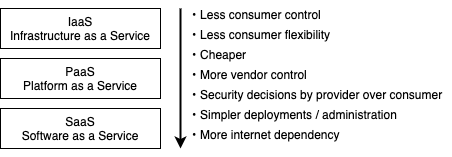
Cloud computing Cloud computing = On-demand access to IT capabilities Before cloud computingEverything was stored and processed locally (on-premises) Centralized, secluded and segmented Now third party (cloud provider) stores the data. NIST definition of cloud computing Essential characteristics On-demand self-service Consumers can unilaterally provision computing capabilitiesE.g. computing power, storage, network Does not require human interaction Broad network access Capabilities are available and accessible over the network. Via wide variety of platforms e.g. laptops, mobile phones and PDAs Resource pooling Uses multi-tenant model to provide resources pooled to serve multiple consumersThe instances (tenants) are logically isolated, but physically integrated. One or multiple instances of one or multiple applications operate in a shared environment. Assigns different physical and virtual resources dynamically Location is abstracted to e.g. country, state or data-centerExact location is unknown to user Rapid elasticity Feeling of "infinite" and instant scalability Usually automatically Measured service Metering capability in an abstracting way e.g. storage, processing, bandwidth, active user accounts. Resource usage can be monitored, controlled, and reported Cloud computing service models Infrastructure as a services (IaaS) Capability for consumers to provision processing, storage, networks, and other fundamental computing resources Aims to give most control over the provided hardware that runs applicationsE.g. operating systems, storage, and networking components E.g. virtual machines (EC2 in Amazon), virtual networks. Provides capability for consumers to deploy onto managed cloud infrastructure Allows consumer to use programming languages, SDKs, services, and tools supported by the provider Consumer does not control or manage underlying cloud infrastructureBut can control deployed applications and configurations for the hosting environment Provides an environment for building, testing, and deploying software applicationsCan add features such authentication. Aims to help creating an application quickly without managing the underlying infrastructure. E.g. development tools, config management, and deployment platforms Software as a Service (SaaS) Software that is centrally hosted and managed for the end customer. User does not control underlying cloud architectureE.g. network, servers, OS, storage etc. Can only control limited user-specific application configurations. IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS
Identity-as-a-Service (IDaaS) Security-as-a-Service (SECaaS) Integrates security services into corporate infrastructure Services include e.g. • penetration testing • authentication • intrusion detection • anti-malware • security and incident management. E.g. McAfee Cloud Security Container-as-a-Service (CaaS) Container and cluster services Services include e.g. • virtualized container engines • easier container and cluster management Inherits features of IaaS and PaaS See also container security Function-as-a-Service (FaaS) Separation of duties Cloud computing is the ultimate in separation of duties E.g.The data owner is the entity accountable for the data itself Data custodian is the entity responsible for access to the data When a single individual becomes both the data owner and the data custodian, security issues can arise. Also a countermeasure for insider attacks and social engineering attacks . Shared responsibility On-premises : you manage everything.IaaS : provider manages virtualization, servers, storage and networkingPaaS : provider additionally manages OS, middleware and runtimeSaaS : provider manages everythingCloud Deployment Models Private cloud Provisioned for exclusive use of single organization May be owned/managed/operated by the organization, third party or combination May be on or off premises Public cloud No local hardware to manage or keep up-to-date, everything runs on your cloud provider's hardware. Services are rendered over a network Provisioned for open use by the general public May be owned/managed/operated by a business, academic, government or combination. Exists on the premises of the cloud provider. Shared infrastructure between several organizations with shared concerns (e.g. compliance) Not open to public May be owned/managed/operated by the organization, third party or combination May be on or off premises Hybrid cloud Composition of two or more cloud (private, community or public) Infrastructures remain unique entitiesbut are bound by a technology allowing data and application portability. Multi cloud Multi-cloud is a environment where an organization leverages two or more cloud computing platforms to perform various tasks Increases capabilities with combined offering Limits data loss and downtime to a greater extent. Management products include • Azure Arc • Google Anthos • AWS Outposts Pros and cons of cloud computing Advantages of cloud computing Economical : Less infrastructure cost, less cost of ownership, fewer capital expensesOperational : cost efficient, elastic, quick provisioning, automatic updates, backup and recovery...Staffing : Less staff is required, less personal trainingSecurity : Patch application and updates, less cost on security configurations, better disaster recovery, audit and monitoring on providers side, better management of security systems.Innovation : Quick access to innovationDisadvantages of cloud computing Organizations have limited control and flexibility Prone to outages and other technical issues Security, privacy, and compliance issues Contracts and lock-ins Depends on network connections Can be hard to migrate from one to another Cloud regulations FedRAMP : US regulatory effort regarding cloud computingPCI DSS : Deals with debit and credit cards, but also has a cloud SIGNIST Cloud Computing Reference Architecture Cloud actors Cloud Consumer User of the cloud products and services Cloud Provider Delivers cloud computing based products and services Cloud Auditor Can conduct independent assessment of cloud services Cloud Broker Manages the use, performance and delivery of cloud services Negotiates relationships between providers and consumers Service categoriesService Intermediation : Improves value of a cloud service/functionService Aggregation : Combining multiple services to a new oneService Arbitrage : Like aggregation but services can be chosen from different vendors. Cloud Carrier Provides connectivity and transport of cloud services from providers to consumers. Service Level Agreement (SLA) Span across the cloud and are offered by service providers Service-level agreement (SLA) is a commitment between a service provider and a client