Risk management
- Ongoing process of identifying, assessing and acting on potential risks.
- ❗📝 Risk management controls reduce risks but one can never fully eliminate all risk
- Nothing is 100% risk-free.
Risk
- Risk
- Threat of damage or loss
- Risk mitigation
- Also known as risk reduction
- Taking action to reduce an organization's exposure to potential risks and reduce the likelihood that those risks will happen again.
- 📝 Risk equation
Risk = Threat x Vulnerability x Asset- E.g. network is very vulnerable (no firewall), asset is critical: high risk.
- E.g. network is well protected, asset is critical: medium risk
- 📝 Likelihood
- Likelihood is how probable it is that an event will occur
- 📝 Impact
- Estimate of the harm that could be caused by an event
Types of risks
- 📝 Inherent risk
- Represents the amount of risk that exists before any controls are taken.
- Raw and untreated risk
- 📝 Residual risk
- Amount of risk that remains after controls are accounted for.
- Control risks
- Risks that occur due to weaknesses in internal controls
- Audit risk
- Risk of error while performing an audit.
- Three types: Control risk, detection risk, inherent risk
- Detection risk
- Verifier does not detect a material misstatement
Level of risk
Defined based on events possible consequences to evaluate.
Level of risk equation
Consequence x Likelihood
Risk Level Consequence Action Extreme / high Serious danger Measures should be immediately taken to reduce the risk Medium Medium danger Measures should be taken as soon as possible Low Negligible danger Preventive measures should be taken to mitigate the risk
Risk matrix
- Used to visualize risk probabilities and its consequences
- Most used method in risk analysis
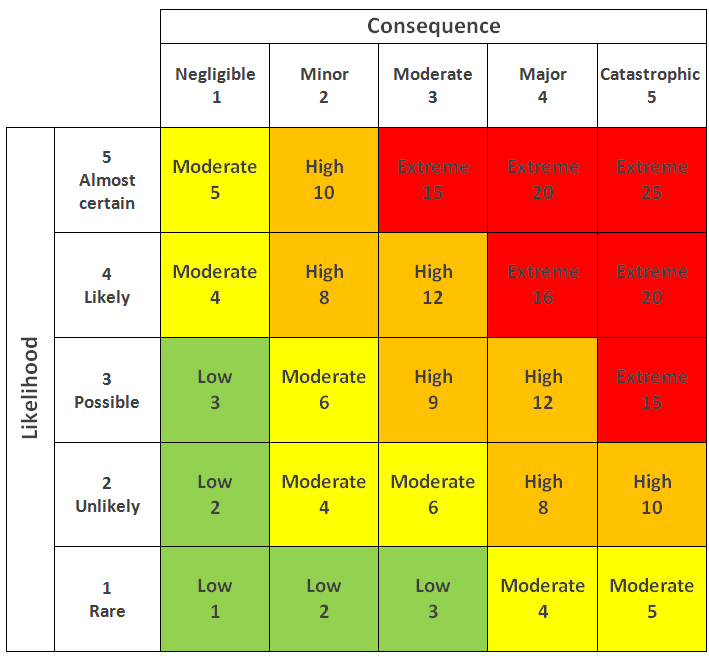
Risk assessment
- 📝 Prioritizes risks based on severity and likelihood of occurrence
- 📝 Includes an analysis of threats based on the impact to the business
- E.g. HIPAA security risk assessment tool to assess risks regarding: • administrative safeguards • technical safeguards • physical safeguards as defined in HIPAA rules.
- 💡 Risk assessor should be a trusted entity or contractor
- As they'll receive detailed vulnerability information and security architecture information
Risk management objectives
- Identify the potential risks
- Identify the impacts of those risks
- Create risk management strategy and plan
- Assign priorities to risks
- Analyze the risks
- Control the risk
- e.g. education, enforcing a policy, changing a software etc..
- Develop strategies and plans for long lasting risks
Risk management phases
- 📝 Identification
- What? Why? Consequences?
- Data gathering activities include • threat identification • vulnerability identification • risk control analysis
- Assessment
- Likelihood and impact
- Treatment
- Prioritize, order and document.
- Manage risks through risk response types
- Tracking and review
- Ensures right actions were taken.
- Is action obsolete? Can it be improved? Can cost be decreased?
Risk responses
- 📝 5 risk responses are: • Avoid • Mitigate • Transfer • Accept • Share
- Avoid
- Change the strategy/plan to avoid the risk.
- Mitigate
- Take action to reduce the risk.
- 💡 You should mitigate the risk to a low enough level so that the residual risk can be accepted as you will never be able to remove all risks.
- Transfer
- Transfer risk to another party by e.g. outsourcing or purchasing an insurance.
- Accept
- Decide to take the risk, as without risk there's no movement/rewards.
- Share
- Distributing the risk, e.g. having two security architects so service can continue if one quits.
Business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR)
- Risk assessment
- Preparing risk analysis and business impact analysis
- See also risk assessment
- E.g. Disaster recovery risk assessment
- Describes potential risks and their impact to the functioning of an organization.
- Describes both natural and man-made disasters and estimates the probability of each scenario occurring
- Business impact analysis (BIA)
- Predicts the consequences of disruption of a business function
- Process and gathers information needed to develop recovery strategies
- Often includes Annualized Loss Expectancy (ALE) metrics.
- Should be used identifying the potential consequences of a change, or estimating what needs to be modified to accomplish a change
- 📝 Business change impact analysis
- Allows you to identify consequences of a change
- E.g. a new feature can cause resource load and crash the server.
- Business continuity plan (BCP)
- Covers critical processes recovery
- 📝 Includes Disaster recovery plan (DRP) describing:
- How an organization can quickly resume work after an unplanned incident
- What to do to recover
Annualized Loss Expectancy (ALE)
- Annual cost of a loss due to a risk.
- Used often in risk analysis and business impact analysis
- 📝
ALE = ARO (Annual rate of occurrence) x SLE (Single loss expectancy) - Annual rate of occurrence (ARO)
- E.g. if it occurs every month than it's 12, if it's every second year than it's 1/2
- Single loss expectancy (SLE)
- Total loss value for a single asset after an exploit
SLE (Single Loss Expectancy) = AV (Asset Value) x EF (Exposure Factor)- Asset value (AV)
- How much would it take to replace 1 asset
- Including product prices, manhours etc.
- Exposure Factor (EF)
- Percentage of asset value lost if threat is realized
- Usually a subjective value
- E.g. an asset is valued at $100,000, and the Exposure Factor (EF) for this asset is 25%. The single loss expectancy (SLE) then, is 25% * $100,000, or $25,000.
- Total cost of ownership (TCO)
- Total cost of a mitigating safeguard
- Return on Investment (ROI)
- Amount of money saved by implementing a safeguard.
- 💡 Good choice if annual Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is less than Annualized Loss Expectancy (ALE); poor choice otherwise
Threat modeling
- Assessment to see how secure an application is
- identify the threats
- can e.g. use OWASP top 10 as guideline.
- discover application vulnerabilities
- improve security
- e.g. configure in better way, improve source code, enable encryption or ditch the application.
- identify the threats
- 💡 Do it as soon as and often as possible
- E.g. by design phase of the software security development lifecycle (SDL) process
Threat modeling steps
- Identify security objectives
- Understand your integrity, confidentiality, and availability goals
- Application overview
- Understand application and its components (libraries and services), data flows and trust boundaries.
- Decompose application
- Document what each component does, entry and exit points, data flows and trust boundaries.
- Identify threats
- Done for each individual components
- E.g. a misconfiguration (e.g. bad password policy, outdated encryption)
- Identify vulnerabilities
- End with vulnerabilities, overall assessment, prioritization of risks.
Security Development Lifecycle (SDL)
- Set of guidance, best practices, tools, and processes by Microsoft
- Consists of different phases with different actions on each phase:
- Training
- Core security training for developers
- Requirements
- Setting level of security desired
- Design
- Threat modeling
- Attack surface analysis
- Requirements
- Implementation
- Static analysis
- Turning off unsafe functions
- Verification
- Dynamic analysis
- Fuzz testing
- Attack surface reviews
- Release
- Incident response plan
- Final security review
- Certification
- Response
- Allow reporting security problems in products
- Training