Escalating privileges
- Exploiting OS and software vulnerabilities to gain admin privileges.
- Generally by executing a malicious code that grant them higher privileges
- Becoming admin on the target system allows all sorts of malicious activities.
Types of privilege escalation
- Horizontal privilege escalation
- Acquiring the privileges of the same level
- Allows executing files from a location that should be protected
- Vertical privilege escalation
- Acquiring higher privileges
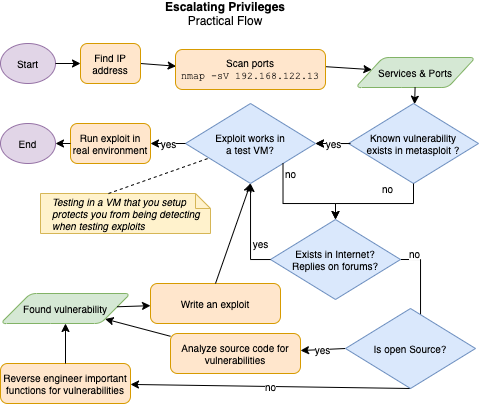
Example flow of escalating privileges
Privilege escalation techniques
- Path Interception
- Creating files at paths to be executed instead of legitimate targets.
- Exploits misconfigurations, quotes, search orders
- Web Shell
- Installed as backdoor to control from a remote server
setuidandsetgid- Setting them allows to execute files with more privileges than user in macOS and linux.
Pivoting
- Using a compromised system as a launching point into other systems.
- E.g. in Metasploit you can add route to first compromised system to access the network beyond it.
Windows techniques
Access token manipulation
- Access tokens are used in Windows as security context of a process or thread
- Every process user executes gets token issued for authentication user.
- User can modify the tokens so processes seem to belong another user.
- E.g. "run as" runs as administrator user therefor giving administrator privileges
File system permissions weakness
- Binaries in Windows execute with privileges of process that's executing it.
- Original binaries can be replaced with malicious ones to privileges
Windows application shimming
- Shim = Windows Application Compatibility Framework
- Compatibility layer for newer/older versions of Windows
- Run in user mode and cannot modify the kernel
- Exploited to e.g. • Bypass UAC (RedirectEXE) • Inject malicious DLLs (InjectDLL) • Capture memory addresses (GetProcAddress)
- Allows attacker to e.g. • Disable Windows defender • Escalate privileges • Install backdoors
Windows applications DLL vulnerability
- Reason: Failure to supply a fully qualified path of a DLL library that is being loaded.
- Behavior: Application looks for the DLL in the directory from which it was executed.
- Vulnerability: Placing a malicious DLL into the directory and gain access to the system.
Scheduled tasks
- Used to escalate privileges, maintain persistence, start at startup etc.
macOS techniques
OS X applications dynamic library vulnerability
- Behavior: OS X looks for dynamic libraries (
dylib) in multiple directories when loading them. - Vulnerability: Injecting malicious
dylibs into one of the primary directories, which will then be loaded instead of the original one.
Launch Daemon
- Allows to execute malicious files at boot-up time.
- Enables escalating privileges, maintain persistence, start at startup etc.
Meltdown vulnerability
- Affects some Intel chips
- Bypasses security mechanisms that prevent programs from reading arbitrary locations in system memory.
- If exploited, it gives attackers ability to read the memory outside of the program
- Allows attackers to
- escalate their privileges
- read information such as credentials, private keys, and so on.
Spectre vulnerability
- Affects modern microprocessors
- Tricks a program into accessing the program's memory space.
- Allows attackers to
- read kernel memory to obtain sensitive information
- use JavaScript to launch a web-based attack
Privilege escalation countermeasures
- Apply least-privilege: Never grant more privileges than needed!
- Use encryption and MFA
- Run services as unprivileged accounts
- Patch and update regularly
- Ensure all executables are write-protected
User Access Control (UAC)
- 📝 Prompts user for potentially dangerous software in Windows
- Limits softwares to user privileges until an administrator authorizes an elevation.
- 💡 Should be set to "Always Notify"
Privilege escalation tools
- BeRoot to check common misconfigurations to find a way to escalate privileges on Linux and Windows
- linpostexp: Linux post exploitation enumeration and exploit checking tools
- Windows Exploit Suggester and Linux Exploit Suggester