Spoofing attacks
- Entails changing a computer's identity
- Allow the bypassing of access control lists on servers or routers
- Allows hiding a device on network by impersonating another network device / system.
IP address spoofing
- Used most commonly in DDoS attacks.
- Helps with overcoming authentication based on IP addresses
- Usually in corporate networks where trust between devices exists
- E.g. accessing intranet without any password.
- ❗ The response is sent to the spoofed IP address instead of the spoofer.
IP address spoofing countermeasures
- Packet filtering by a gateway
- Ingress: block packets from outside of the network having an IP address within the network.
- Egress: block outgoing packets from inside with a source address that is not inside
- 💡 Design network protocols and services so that they do not rely on the source IP address for authentication.
- Sequence number
- Used by upper layer TCP
- Negotiated to ensure that arriving packets are part of an established connection.
- 📝 Must be guessed in order to hijack the connection
MAC spoofing
- Response is received to spoofing party as opposed to IP address spoofing
- See also MAC | MAC flooding | Sniffing attacks
MAC spoofing use-cases
- New hardware for existing Internet Service Providers (ISP) where ISP charges per device.
- Fulfilling software requirements where one software can only be installed on a single device.
- Identity masking for pushing responsibility for other users.
- MAC address randomization: Implemented in Android, Linux, iOS, and Windows to prevent third parties from using the MAC address to track devices
MAC spoofing attack
- Flow
- Attacker sniffs the network for MAC addresses of legitimate users
- Spoofs one of those addresses
- The attacker receives the traffic intended for that user
- Effective against MAC filtering
- E.g. using
ifconfigifconfigto get name of network interface e.g.eth0ifconfig eth0 downto deactivate it to be able to change it (will lose connection)ifconfig eth0 hw ether 88:88:88:88:88:88to change the MAC addressifconfig eth0 upto change the MAC address
- E.g. using macchanger
-rto get a random MAC address e.g.macchanger -r eth0-mset specify MAC address manually to pretend to be someone else
STP spoofing
- STP: Spanning tree protocol
- Layer 2 link management protocol
- Provides path redundancy while preventing loops in the network
- Allows intercepting traffic when attacker emulates a device with a (lower) root switch identifier
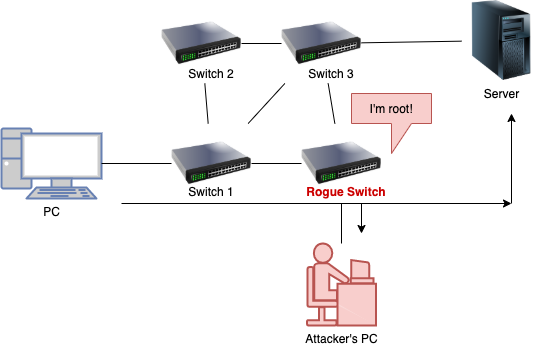
STP spoofing attack
- Also known as STP manipulation attack, STP attack or STP root role attack.
- Flow
- Attacker introduces a rogue switch
- Switch advertises superior BPDUs to force a STP recalculation
- BPDU = Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs)
- Frames that contain information about STP that's between exchanged switches
- BPDU = Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs)
- Rouge router becomes elected as root switch
- All the traffic will cross this switch giving the attacker possibility to sniff all traffic in the company
- Allows for
- DoS attacks
- Recalculation of STP have interruption on the system as the root bridge changes
- Just sending BPDU messages would be enough as becoming root is not needed.
- MITM attacks
- Also known as dual-homing (dual-homed)
- Attacker uses two interfaces, one to win the root other to send data to the attacker.
- 📝 Attacker can configure one of the switch ports as a SPAN port to receive copy of the traffic.
- DoS attacks
- Mitigations
- Enable Root Guard to not forward traffic to port with superior BPDUs
- Enable BPDU Guard to enforce the STP domain borders
IRDP spoofing
- IRDP: ICMP Router Discovery Protocol
- Protocol for computer hosts to discover routers on their IPv4 local area network.
- ICMP router discovery messages are called "Router Advertisements" or "Router Solicitations"
- Vulnerable as it does not have any validation
- Attacker needs to be in the same network as the victim.
- Attacker adds bad route entries into a victim's routing table redirecting victim traffic to malicious address.
- Allows
- Passive sniffing through rerouting victim machine to attacker machine
- Man-in-the-middle where attacker acts as proxy
- DoS by flooding wrong entries
- Countermeasures
- Disable IRDP
- Use digital signatures
- Block all type 9 and type 10 ICMP packets.